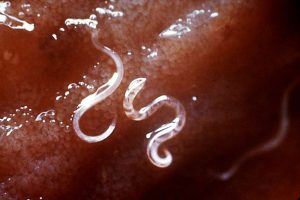
 Ancylostoma duodenale is a type of parasitic hookworm that infects the small intestine of humans, causing a condition known as hookworm infection or ancylostomiasis. This parasite is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in areas with poor sanitation. Infection occurs when larvae in contaminated soil penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet. Once inside the body, the larvae travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, are swallowed, and mature into adult worms in the intestines. Symptoms include anemia, fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and in severe cases, malnutrition, especially in children.
Ancylostoma duodenale is a type of parasitic hookworm that infects the small intestine of humans, causing a condition known as hookworm infection or ancylostomiasis. This parasite is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in areas with poor sanitation. Infection occurs when larvae in contaminated soil penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet. Once inside the body, the larvae travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, are swallowed, and mature into adult worms in the intestines. Symptoms include anemia, fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and in severe cases, malnutrition, especially in children.
Clearing Ancylostoma duodenale involves using antiparasitic medications such as albendazole or mebendazole. Treating the infection improves iron levels, reduces anemia, and restores overall health. Preventing hookworm infection through improved sanitation, wearing footwear, and regular deworming programs can significantly reduce the disease burden in affected areas. Restoring health after hookworm infection can lead to improved energy levels, better cognitive development in children, and enhanced quality of life.



