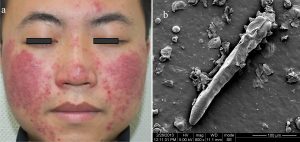
 Demodex folliculorum is a microscopic mite that lives in the hair follicles of humans, primarily on the face, including the nose, cheeks, forehead, and eyelashes. While most people harbor these mites without symptoms, an overpopulation can lead to a condition called demodicosis, which is associated with various skin issues. Demodicosis is particularly common in individuals with weakened immune systems or those with underlying skin conditions like rosacea.
Demodex folliculorum is a microscopic mite that lives in the hair follicles of humans, primarily on the face, including the nose, cheeks, forehead, and eyelashes. While most people harbor these mites without symptoms, an overpopulation can lead to a condition called demodicosis, which is associated with various skin issues. Demodicosis is particularly common in individuals with weakened immune systems or those with underlying skin conditions like rosacea.
The presence of excessive Demodex folliculorum mites can cause symptoms such as itching, redness, inflammation, and scaly or rough skin. The mites contribute to blocked follicles, which can trigger acne-like eruptions and exacerbate conditions like rosacea, blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids), and seborrheic dermatitis. In severe cases, individuals may experience discomfort and emotional distress due to visible skin abnormalities.
Treatment of demodicosis involves topical medications such as metronidazole, ivermectin, or sulfur-based creams, which reduce the mite population. In some cases, oral antiparasitic medications may be prescribed. Maintaining good facial hygiene, avoiding heavy cosmetics, and treating underlying skin conditions can help prevent mite overgrowth. For individuals with recurrent or persistent symptoms, regular skin care routines and targeted treatment offer significant relief and improve the appearance and health of the skin.



