 Trombiculidae, commonly known as chiggers, are the larval stage of certain mites that cause trombiculiasis through their bites. These mites are most active in grassy or wooded areas and attach to the skin of humans and animals when passing by. Chiggers do not burrow into the skin; instead, they inject digestive enzymes into the skin to break down tissue, which they feed on. This process causes intense itching and skin irritation.
Trombiculidae, commonly known as chiggers, are the larval stage of certain mites that cause trombiculiasis through their bites. These mites are most active in grassy or wooded areas and attach to the skin of humans and animals when passing by. Chiggers do not burrow into the skin; instead, they inject digestive enzymes into the skin to break down tissue, which they feed on. This process causes intense itching and skin irritation.
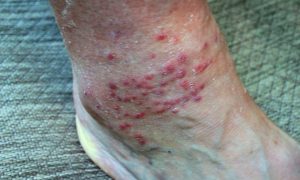
The primary symptom of trombiculiasis is severe itching accompanied by small, red, raised bumps that often develop into a rash. Chigger bites are commonly found in areas where clothing fits tightly, such as the waist, ankles, and underarms. Scratching the bites can lead to skin infections or more severe reactions in sensitive individuals.
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms with topical anti-itch creams, such as hydrocortisone, or antihistamines to reduce inflammation. Washing the affected area with soap and water immediately after exposure can help remove any remaining mites. Preventing chigger bites involves wearing protective clothing, applying insect repellents, and avoiding areas with heavy vegetation. Properly treating outdoor clothing and gear can further minimize the risk of infestation.



